Updated April 2023
Access to maternity care is key to addressing the maternal mortality crisis. Midwife services can bridge gaps in health care, reduce health disparities, and support maternal and neonatal well-being.
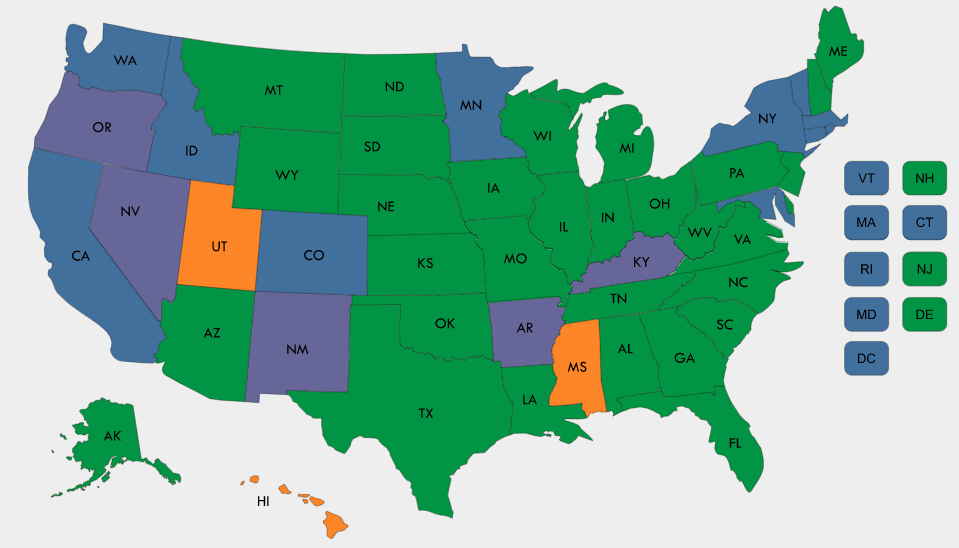
This interactive map summarizes state Medicaid reimbursement policies for all types of midwives including certified nurse-midwives (CNMs) and midwives who pursue alternative pathways to licensure, often referred to as certified professional midwives (CPMs), certified midwives (CMs), or direct entry midwives depending on state regulations.
The accompanying tables provide a detailed description of individual state midwife policies, including licensure for some midwives. You can also download the charts on Certified Nurse-Midwife State Medicaid Reimbursement Policy and Midwife Licensing and State Medicaid Reimbursement Policy.
Read the accompanying case studies: Improving Birthing Outcomes through Midwifery Care: New Mexico and Medicaid Reimbursement of Midwifery Services in Minnesota and Washington State Supports Diverse Pathways to Care.
Read the accompanying policy brief: Medicaid Financing of Midwifery Services: A 50-State Analysis.
For questions or updates related to this research, please reach out to Anoosha Hasan at ahasan@nashp.org.
Definitions
For the purposes of this chart and map:
- Midwives refers to midwives without a nursing degree. Terminology for midwives without a nursing degree varies across states. Examples include: licensed midwives, direct entry midwives, certified professional midwives, and more.
- Certified nurse-midwives refers to midwives with a nursing degree.
-
Certified Nurse-Midwife State Medicaid Reimbursement Policy
-
Midwife Licensing and State Medicaid Reimbursement Policy
| State | Independent or Collaborative Practice | Medicaid Payment and Delivery | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNM Medicaid Reimbursement | CNMs Can Serve as PCP in Medicaid | Global Maternity Payment includes CNM Services | Expanded CNM Services Reimbursed | Specific CNM Fee Schedule | CNMs Included as Eligible Providers in Medicaid Payment Reform Initiatives | ||
Alabama
|
| Y (80% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y
| N | Y |
Alaska*
| Independent
| Y (85% of physician rate)
| Y | N | – | N
| – |
Arizona*
| Y (90% of physician rate) | Y | Y | – | N | Y | |
| Arkansas* | Collaborative | Y (80% of physician rate) | N | N | – | – | |
California | Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| Colorado* | Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | N | – | – | N | Y |
| Connecticut | Collaborative | Y (100% of physician rate) | N | Y | Y | N | Y |
| Delaware* | Collaborative | Y (100% of physician rate) | N | – | – | N | – |
| District of Columbia | Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | N | N | N | N |
| Florida | Hybrid model (restrictions in place) | Y (80% of physician rate) | N | N | Y (Healthy Start Prenatal Risk Screening (SUD/mental health screening) and Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment or SBIRT) | Y | N |
| Georgia | Collaborative | Y (100% of physician rate) | N | Y | Y (Screening and care coordination; for treatment services, CNMs refer the members to substance use or mental health professionals) | N | N |
| Hawaii | Independent | Y (75% of physician rate) | Y | Y (Pregnancy and delivery are covered as a global service) | Y | N | N |
| Idaho | Independent | Y (85% of physician rate, except for services provided in a RHC, FQHC, or Indian Health Service) | N | Y | N | N | Y |
| Illinois | Collaborative | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | N | Y | N | N |
| Indiana | Collaborative | Y (75% of physician rate) | Y (Within managed care programs) | N/A | Y (Well woman exams and family planning. Depending on qualifications, some may provide SUD and other behavioral health services) | N | Y |
| Iowa | Independent | Y (85% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y (SUD screening and treatment, mental health screening and treatment, and care coordination) | N | Y |
| Kansas | Y (75% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y | N | N | |
| Kentucky | Collaborative | Y (75% of physician rate) | Y | N | Y (Additional services may be approved on a case-by-case basis by the Medical Director) | N | N |
| Louisiana | Collaborative | Y (80% of physician rate; 100% for: EPSDT services, physician administered medication, and long-acting reversible contraceptives) | N | N | Y (Physical and some behavioral health services) | N | Y |
| Maine* | Independent | Y | – | – | – | – | – |
| Maryland | Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | N | Y (SUD screening and treatment, mental health screening and treatment, and care coordination paid as part of enriched maternity services) | N | Y (CNMs are considered eligible providers for certain VBP metrics). |
| Massachusetts | Collaborative | Y (85% of physician rate) | Y | Y | N | Y | Y |
| Michigan | Collaborative | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y (Behavioral health, reproductive health, and SUD screening and treatment services) | Y | N |
| Minnesota | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | |
| Mississippi | Collaborative | Y (90% of physician rate) | N | N | Y (SUD screening and home visiting services) | N | Varies by Coordinated Care Organization (CCO) |
| Missouri | Collaborative | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y (This applies to vaginal deliveries. CNMs are not allowed to bill for Caesarean Section global payments) | Y (Family planning, counseling, birth control technique well-woman gynecological care, and some infant care midwife services) | Y | Y |
| Montana | Independent and/or collaborative | Y (90% of physician rate) | N | Y | Y (Mental health screening and treatment, and caregiver health risk assessment) | N | N |
| Nebraska* | Collaborative | Y | – | – | – | – | – |
| Nevada* | – | Y | – | – | Y (Smoking cessation services, home visiting services) | – | – |
| New Hampshire | Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | N | Y | Y (SUD screening, mental health screening, well woman exams, family planning) | N | N |
| New Jersey* | Independent | Y (95% of physician rate) | – | – | – | – | – |
New Mexico
| Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y (Same as physician covered services) | N | N |
New York* | Independent | Y (85% of physician rate) | Y | – | – |
| – |
| North Carolina | Collaborative | Y (98% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y (SUD screening, mental health screening, care management for high risk pregnancies (CMHRP))
| Y | Y |
North Dakota
| Independent
| Y (75% of physician rate for FFS; 85% of physician rate for MCO)
| Y
| Y (MCO); N (FFS) | Y | N | Y (MCOs); N (FFS) |
Ohio | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y (Depending on service setting) | N | Y | |
| Oklahoma | Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | N | Y | Y (SBIRT, smoking cessation) | N | N |
Oregon | Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y (Global OB package applies when all prenatal care, delivery, and postpartum care is provided by one midwife) | Y (Depending on service setting) | N | N |
Pennsylvania | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y (SUD screening and treatment, mental health screening and treatment, care coordination (service referral), tobacco cessation counseling) | N | Y | |
Rhode Island | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y (SUD screening, mental health screening, care coordination (service referral) | N | Y | |
South Carolina | Collaborative | Y (100% of physician rate) | N | N | N | N | |
| South Dakota | Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y (Mental health screening) | N | Y |
Tennessee | Collaborative | Y (% varies by MCO) | Y | Y | Y (Reimbursable services vary by MCO) | Varies by MCO | Y |
| Texas | Collaborative | Y (92% of physician rate, except 100% of physician rate for laboratory services, x-ray services) | Y (MMC) | N | Y (See the Texas Medicaid Provider Procedures Manual for CNM reimbursable services) | Y (Varies by MCO) | |
Utah | Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y (SUD screening, mental health screening and treatment, other reproductive health services) | N | N | |
Vermont | Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | Y | Y | Y | N | Y |
Virginia | Hybrid model (restrictions in place) | Y (100% of physician rate) | N | N (FFS); Y (Varies by MCO) | N (FFS); Y (MCO) (Well woman exams and family planning) | N | N (FFS); Y (Varies by MCO) |
| Washington | Independent | Y | Y | Y | Y (SUD screening, mental health screening, care coordination service referral) | N | Y |
West Virginia* | Y (100% of physician rate) | – | – | – | N | – | |
Wisconsin | Collaborative | Y (90% of physician rate; 100% if CNM holds a Master’s degree) | Y | Y | N | Y | |
Wyoming | Independent | Y (100% of physician rate) | N | Y | Y (SUD screening) | N | N |
| State | Type of Midwife | Licensing Board/ Licensure Requirements | Medicaid Payment and Delivery | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Midwife Medicaid Reimbursement | Provider Requirements | Global Maternity Payment includes Midwifery Services | Expanded Midwifery Services Reimbursed | Midwife-Specific Fee Schedule | Midwives Included as Eligible Providers in Medicaid Payment Reform Initiatives | |||
| Alaska* | Direct Entry Midwife | Y | – | Y | – | Y | – | |
| Arizona* | Licensed Midwife | Bureau of Special Licensure, Arizona Department of Health Services | Y | – | N | – | Y | N |
| California | Licensed Midwife | Y | Enrollment requirements | N | Y | N(Fall under Non Physician Medical Practitioner) | N | |
| District of Columbia* | Certified Professional Midwife | Y | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Certified Midwife | Y | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| Florida | Licensed Midwife | Department of Health: Council of Licensed Midwifery | Y | Enrollment in Medicaid with appropriate licensure | N | Y (Prenatal risk and SUD/mental health screening) | Y | N |
| Louisiana | Licensed Midwife | Louisiana State Board of Medical Examiners | Y (Covered vaginal delivery services only when provided at a Medicaid Free-Standing Birthing Center) | Enrollment in Medicaid with the appropriate licensure and certification | N | N | N | N |
| Minnesota | Traditional Midwife | Y | Enrollment requirements | Y | Y (Any services that are billable by a free-standing birth center are reimbursable for a midwife) | N | N | |
| Montana | Direct Entry Midwife | Y | – | Y | N | Y | N | |
| New Hampshire | New Hampshire Certified Midwife (NHCM) | Y | Requirements | Y | N | N | N | |
| New Jersey* | Certified Professional Midwife | Y | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Certified Midwife | Y | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| New Mexico | Licensed Midwife | New Mexico Department of Health Public Health Division Maternal Health Program | Y | Requirements | Y (See Supplemental 19-03) | Y (Family planning services) | Y | N |
| New York* | Licensed Midwife | Y | – | – | – | Y | – | |
| Oregon | Licensed Direct-Entry Midwife | Y | Requirements | Y (Oregon’s FFS program pays the same global maternity rate regardless of provider type or setting. Since community birth is carved out of managed care (CCOs), the global payment is the same for all providers including licensed direct- entry midwifes.) | Y (Family planning services) | N | N | |
| South Carolina | Certified Professional Midwife | South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control (SCDHEC) | Y | Must meet SCDHEC requirement. Then goes through standard Medicaid provider enrollment process. | N | N | Y | N |
| Texas | Licensed Direct-Entry Midwife | Y (70% of physician reimbursement rate) | N | Y | Y | Y | ||
| Vermont | Licensed Midwife | Y | They must enroll to be a Vermont Medicaid provider and meet all the requirements of 42 CFR § 455 Subpart B and E. | Y | Y | N | Y (OneCare network) | |
| Virginia | Licensed Midwife | Y | FFS: The requirement is that the provider is licensed as a Nurse Practitioner by the Department of Health Professions with the specialty of Certified Nurse Midwife. Managed Care: MCOs do not contract with non-certified nurse midwives. | N/A | N/A | N | N/A | |
| Washington | Licensed Midwife | Y | Active licensure with DOH and be a contracted provider with Medicaid. | Y | Y (SUD screening, mental health screening) | Y | Y | |
| Wyoming | Licensed Midwife | Y | Enrollment application completed with a copy of licensure/certification and financial forms. | Y | N | N | N | |
Notes
In these tables, “-” indicates information is not available and “*” indicates the information NASHP compiled about this state was publicly sourced but not confirmed by the state’s Medicaid agency.
The Midwife Licensing and State Medicaid Reimbursement Policy table only includes states that provide Medicaid reimbursement for services performed by midwives (Certified Professional Midwives or Certified Midwives).
Acknowledgements
Emily Creveling, Anoosha Hasan, and Taylor Platt contributed to this publication through research. Carrie Hanlon and Karen VanLandeghem provided guidance and review. NASHP thanks the state Medicaid officials for their review. This 50-state analysis was made possible by the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA).